- Electrical Test and Tagging Service
- Welding Equipment Repair and Calibration
- Flashback Arrestor Testing
- Welding Automation
- Laser welder Sales and Repair
- Design & Manufacture Welding Machines
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)
- Finance Options
- Welding Training,Troubleshooting and Demonstration
- Gas Line Manifold, Regulators and Alarm Installation
- Welding Equipment Machines
- Laser Welder/Cutter/Seam cleaner/Cleaner
- Bossweld Machines
- BT Welders
- Easybeat Machines
- ESAB Machines
- Kemppi Machines
- Lincoln Machines
- Miller Machines
- Pin Insulation Welder
- Riland Machines
- Spot Welders
- Stud Welders / Studs / Chucks / Stud Guns
- Steel Vision Machines
- Thermacut Extrafire Plasma Cutters
- Unimig Machines
- UNIMIG Multi-Process Welders
- UNIMIG Plasma Cutters
- UNIMIG CNC Tables
- UNIMIG MIG (GMAW) Welders
- UNIMIG TIG (GTAW) Welders
- UNIMIG Air Compressor
- UNIMIG MMA (STICK) Welders
- UNIMIG Pulse MIG Welders
- UNIMIG Trolleys
- UNIMIG Foot Controls/Remote Controls
- UNIMIG Electrode Ovens
- UNIMIG Water Coolers
- UNIMIG Fume Extraction Unit
- Weldclass Machines
- WIA Machines
- Weld Cleaning Machine
- Duralloy Machines
- Robot Welding Systems
- Trolley
- Foot Controls/Remote Controls
- Fume Extraction Fans Units
- Lincoln Electric Fume Extraction Units
- ITM Fume Extraction Units
- Allclear / Weldclass Fume Extraction Units
- Binzel Fume Extraction Units
- Unimig Fume Extraction Units
- Kemper Fume Extractor
- Bomaksan / Nederman / AWS Fume Extraction units
- Fanmaster Fume Extraction Units
- Translas Fume Extraction Units
- Keller Fume Extraction Units
- BT Fume Extraction Units
- Water Coolers / Chillers/coolant
- Rotators Positioners Torch Holders
- Tungsten Grinders
- Electrode Ovens
- CNC Laser / Plasma
- Welding Carriages / Automation
- Thermocouple Welding Machines
- Plastic Welding
- Induction Welders
- Welding Table Bench
- Pipe welding
- Welding Accessories & Spare Parts
- Feed Rollers / Drive Gears
- Engineers Chalk / Pencils
- Welders Aids Tools
- Electrode Holders
- Chipping Hammers
- Welding Cables
- Earth/Ground Clamps
- Cable Connectors
- Welding Leads Sets
- Balancers
- Gas Solenoids
- Tip Cleaners
- Marking
- Pipe Welding Tools
- LEATHER COVER For MIG / TIG / Torch / PLASMA
- Spool Hubs
- Interconnection Cable
- Purge Gas Retaining Tape for Clean Contaminant-Free Welding / Ceramic Backing Bar
- Welding inspection Gauges
- Flange alignment tools
- Welding Consumables
- MIG Wires
- TIG & Gas Filler Rods
- Aluminium TIG Filler Rods
- Galvanising Bars
- Manganese Bronze
- Nickel Bronze
- SealCore low temperature Aluminum Tig 0r solder Rod 3.2 mm Dia
- Silicon Bronze Tig/solder
- Silver Brazing Alloys
- Soft Solder
- Stainless Steel TIG Rod
- Steel / Black Mild Steel
- Tobin Bronze
- Chrome Molybdenum
- Nickel Alloy
- Die Steel
- De-Oxidised Copper
- Aluminium Bronze Filler Rods
- Phosphor Bronze
- ROD GUARD CANISTERS
- Aluminium Brazing Rods
- Tungsten Electrodes
- Ceriated Tungsten Electrodes
- E3 Tungsten Electrodes 3% Rare Earth
- Lanthanated / Gold / Blue Tungsten Electrodes
- Multi Pack Tungsten Electrodes
- Thoriated Tungsten Electrodes
- Zirconiated Tungsten Electrodes
- Tig Rod / Wire Feeder
- Tungsten Sharpeners
- Tungsten Canisters
- WP2 Green Tungsten Electrodes WITSTAR®
- Electrodes (Welding Rods) ARC / MMA / Stick
- General Purpose Welding Rods E6012 , E6013
- Hydrogen Controlled Welding Rods E7016,E7018
- Cast Iron Welding Rods Ni 55, Ni 98 , Ni 99
- Dissimilar Metals Steel Welding Rods E312-16
- Aluminium Welding Rods 4043
- Stainless Steel MIG Wires ER308, ER309,ER316 Lsi ER2209
- Hard Facing Solid Welding Rods H350,H600,700,43
- Iron Powder Welding Rods E7014 , E7024
- Cellulose Rods E6010 , E6011 , E7010 , E8010
- Low Alloy Welding Rods E8015, E8018 , E9018
- Welding Rod Guard Canister & Hotbox
- Gouging & Hot Rod
- Welding Guns, Torches & Consumables
- Plasma Cutting Torches & Parts
- Autogen Ritter Torches
- Binzel Style
- Cebora Style
- Lincoln Plasma Parts
- THERMACUT Hypertherm Consumable
- Air Filters Plasma
- Trafimet (Bossweld , Cigweld & Unimig) Plasma Torches
- Plasma Cutting Guides
- Unimig Plasma Torches & Parts
- WIA Plasma Torches & Parts
- Plasma Torch & Parts - Weldclass
- Thermal Dynamics SL60/SL100 Plasma Parts
- MIG Torch Spares Parts
- TIG Torch Parts
- Unimig TIG Torch Parts & Consumables
- Clear Pyrex Cup Kits
- Stubby 17/18/26 TIG Setups
- 9 Series Torch Bodies
- 17 Series Torch Bodies
- 26 Series Torch Bodies
- 20 Series Torch Bodies
- 18 Series Torch Bodies
- Back Caps For Tig 9/17/18/20/26
- Binzel TIG Torch Parts & Consumables
- 9/20 Series Collet Bodies
- 9/20 Series Gas Lens
- 17/18/26 Series Gas Lens Alumina Cup
- TIG Fingers
- 9/20 Series Gas Lens Alumina Cups
- 17/18/26 Series Insulators
- 9 Series / 17 Series Parts
- 17/18/26 Series Collets
- 17/18/26 Series Collet Bodies
- 17/18/26 Series Gas Lenses
- 17/18/26 Series Collet Body Alumina Cups
- 9/20 Series Insulators
- Accessory Kits
- 9/17/20/24 Series Parts
- 9/17/24 Series Parts
- TIG Torch Adaptors
- 9/20 Series Collet Body Alumina Cups
- 9/17/18/24/26 Series Parts
- 9/20 Series Collets
- 26 Series Parts
- 18/20 Series Parts
- 20/24 Series Parts
- TIG Torch Switches
- T2 / T3 / T3W Tig Torch Parts
- MICRO TIG Parts
- TIG Spare Parts / Consumables KIT
- TigWare Products
- Gouging / Gouging Torches
- MIG Torch
- TIG Torches
- i HEAD
- Plasma Cutting Torches & Parts
- Sale
- Package Deal / Clearance /Sale
- Gas / Trolleys / Accessories
- Gas Welding : Cutting/ Heating/ Regulators
- Harris
- Kits
- Gas Cutting Machines
- Harris Medical
- Hose and Cord Reels
- Cutting Attachments/ Torches
- Handles
- Mixers
- Heating Tips
- Welding and Brazing Tips
- Flashback Arrestors & Testers
- Accessories
- Cutting / Gouging Nozzles
- Heating Torches Kit
- Supa Heat Heating Barrels
- Gas Hose /Assemblies
- CO2 Heaters / Gas Heaters
- Gas Regulators
- Gas Hose Fittings
- Gas Cutting Guides
- Soldering Iron Gas
- Swirl Tips
- Thermic Lance Kits
- Manifold Cylinder /Connection Leads /Scientific Equipment
- Spray Torches
- Gas Fittings
- Gas Purging Systems
- Tools / Power Tools
- ITM Tools
- ITM Complete Product and Price List
- Benders ITM
- Vices ITM
- Generators ITM
- Air Compressors ITM
- Grinding Machines ITM
- Fans and Ventilators ITM
- Drilling Machines ITM
- Air Tools & Accessories ITM
- Bevelling Machines ITM
- Brushware ITM
- Engineers Tools ITM
- Hand Tools ITM
- Measuring Tools ITM
- Metal Cutting Saws ITM
- Punches & Shears ITM
- Sharpening Machines ITM
- Spray Equipments ITM
- Striking Tools ITM
- Welding Carriages ITM
- Clamps ITM
- Cutting Tools ITM
- Brushware
- Workshop Storage
- Water Pumps ITM
- Pressure Washers ITM
- Lifting & Rigging ITM
- Ratchet Tie Downs ITM
- WELDING CARRIAGES ITM
- ITM Holemaker
- Kincrome Tools
- Agriculture & Farming Kincrome
- Air Tools & Accessories Kincrome
- Automotive & Vehicle Servicing kincrome
- Construction Kincrome
- Striking & Prying Kincrome
- Cut, Scrape & Saw kincrome
- Lifting & Materials Handling Kincrome
- Lighting & Electrical Kincrome
- Lubrication & Fluid Transfer Kincrome
- Measuring, Marking & Layout Kincrome
- Pliers & Wrenches kincrome
- Power Tools & Accessories Kincrome
- Recreation & Lifestyle
- Screwdrivers & Fastening Kincrome
- Sockets, Socket Sets & Accessories Kincrome
- Spanners & Spanner Sets Kincrome
- Tool Boxes & Storage Kincrome
- Tool Kits & Sets Kincrome
- Workshop & Engineering Kincrome
- Kincrome price list
- Merchandise & Apparel
- Pressure Washers
- File Kincrome
- Metabo Tools
- Impact Wrenches
- Outdoor Power Equipment Metabo
- Paint Stripper
- Heater/ Glue Guns
- Die Grinder Cordless
- Belt Sander Cordless
- Heating Jackets
- Site Lighting Metabo
- Vacuum Cleaners and extractions Metabo
- 18v CORDLESS METABO
- 18v KIT METABO
- ANGLE GRINDER 240V METABO
- Accessories/Abrasives Metabo
- DRILL 240v METABO
- Sawing Metabo
- Nail Gun Metabo
- Bevelling Tool Metabo
- Burnisher Metabo
- Metal Processing Metabo
- Batteries Metabo
- Chargers Metabo
- FEIN TOOLS
- Makita Tools
- Warren & Brown
- National+
- FESTOOL
- KC Tools
- Katana
- Sutton Tools
- Files & File Sets P&N
- Scribers P&N
- Countersinks
- Drills
- Drill Sets Jobber set
- Holesaws Sutton
- Bolt Extractors
- Recoil
- Literature
- Taps
- Pliers & Wrenches
- Deburring Sutton Tools
- Adaptors SUTTON TOOLS
- Snips & Shears SUTTON
- Measuring Tools P&N
- Chisels sutton tools
- Die / Die Nuts
- Pipe Threading Sutton
- Clamps Sutton
- Saw Blades CarbiTools
- Screwdriver Bits
- Carbide Burrs Sutton Tools
- Holemaker Magnetic Base Drilling Systems
- Toledo
- Matson
- Strong Hand Tools
- ACCUD Tools
- Milwaukee Tools
- BOSCH Tools
- Tolsen Tools
- Excision
- Industrial Clamps Excision
- Annular Cutters/Core Drills & Accessories Excision
- Magnetic Based Drills Excision
- Punching Machines Excision
- Metal Cutting Machines Excision
- Coolants Excision
- Punches and Dies Excision
- Bandsaw/Coldsaw/TCT Circular Blades Excision
- Coldsaw Machines
- Bevellers Excision
- Taps Excision
- Blades Excision
- Stanley
- Alpha/Sterling/AustSaw
- Lufkin
- Metrinch
- Lasquare
- Shinano
- Komelon
- Garrick
- Maxigear / Precision
- Dawn
- Magswitch MSA Magnetics
- Nitto Kohki
- Thor Hammer
- Abbott & Ashby
- Action Tools
- Bordo Tools
- DeWALT
- M7 Air Tools
- BRAMLEY Tube bender
- Mako Tools
- Prowin Tools
- Band Saw Blade
- Hikoki Tools
- Estwing
- Starrett
- Bondhus
- KNIPEX
- Durum
- NPK Tools
- Geiger Tools
- Alliance Tools
- Mumme Tools
- Klein Tools
- Hyundai Power Tools
- Teng Tools
- LENOX Tools
- ITM Tools
- Sheet metal Bending and Folding
- Safety / PPE
- Welding Helmets
- Welding Helmet Spare Parts & Accessories
- Easybeat Welding Helmet
- Unimig Welding Helmet
- Lincoln Welding Helmet
- Speedglas™ 3M™ Welding Helmet
- Bossweld Welding Helmet
- Miller Welding Helmet
- WIA Welding Helmets
- Optrel Welding Helmets
- Kemppi Welding Helmets
- Weldclass Welding Helmets
- Tecmen Welding Helmets
- General Safety Gear
- Hearing Protection
- Eye / Face wear
- Head Protection
- Coveralls
- Respiratory Gear
- Sun Protection
- Gloves
- Welding Jackets
- High VIS Clothing
- Welding Goggles
- Welding Screens & Frames
- Welding Blankets
- Roofers Kits
- Welding Sleeve
- Welding Hood
- Welding Apron
- Footwear
- Spats And Knee Pads
- Lincoln
- Security Padlocks
- Heavy Duty Umbrella
- Spill Control & Containment
- Safety Trousers
- AntiSlip
- Welding Helmets
- Abrasives
- 3M Abrasives
- Flap Discs 3M™
- Scotch-Brite™ Clean & Strip Discs
- Cubitron™ Fibre Disc
- Scotch-Brite™ Hand Pads
- Cubitron™ Grinding Wheel
- 3M™ Cut-Off Wheels
- Scotch-Brite™ Light Grinding and Blending Disc
- 3M™ Belts
- Silver Depressed Centre Grinding Wheel
- 3M Bristle Brushes and Discs
- 3M Bonding/Mounting/Transfer Tapes
- 3M Cubitron™ Cut-Off Discs
- 3M Compounds & Polishes
- Abrasive Sheets & Rolls 3M
- Deburring & Finishing Wheels 3M
- Pferd Abrasives
- Klingspor Abrasives
- Norton Abrasives
- Flexovit Abrasives
- Grinding Discs
- Flap Discs
- Cutting Discs
- Clean & Strip DC Discs
- Fibre Discs
- Wheel Brushes
- Pipeline Brushes
- Bevel Brushes
- Cup Brushes
- Spindle Mounted Brushes
- Hand / Wire Brushes
- Tube Brushes
- Handy Rolls
- Fan Wheels
- Comidisc / Fine Grinding & Polishing
- Linishing Belt
- Sanding Discs
- Diamond Blades
- Spiral Band
- Backing Pads
- Mounted Points
- Small Abrasives Mop
- 3M Abrasives
- Generators
- Air Compressors & Accessories
- Chemicals
- Anti Spatters
- Belt Conditioner
- Nozzle Dips
- Flux Welding
- Chain & Cable Lube
- Chrome Cote Paint
- Cobra Cote Vinyl Cleaner
- Electric Component / Cleaners
- Glass Cleaners
- Liquid Spanner
- Multi Lube Spray
- Slipe Slide and Glide
- Supa Squirt
- Paint: Cold Galvanising/Silver Gal & Paint
- Crack Detector / Dy Check/Flawcheck
- Weld Cleaning
- Gasket Makers & Sealants
- Activators / Cleaners
- Anti Seize
- Molyslip
- Cutting, Buffing & Polishing Compounds
- Hand Cleaner
- Top Guard Gel Coat Treatment
- Woolube
- Multi Purpose Lubricants
- Degreaser & Parts Washer
- Stainless Steel & Metal Cleaning Products
- Cutting Fluids,Compound
- Pickling Paste Gel
- Aluminium Brightener & Cleaner
- Grease Fleece Silicone/Lubrication
- Tape
- Rust Remover
- OIL
- Brake And Parts Cleaner
- Truck Wash
- Coolant
- Flece Grease
- CRC
- Marking products
- Aero Spark
- Concrete Dissolver/Remover
- Jet Ski & Boat Marine
- Electrical
- Clamps
- Air Tools (Pneumatic Tools)
- High Pressure Cleaners / Sweepers
- Panel Beating & Smash Repair Products
- Machinery Tools
- Storage Cabinets
- Lubrication and Fluid Transfer wax
- Drill / Hole Saws / Annular Cutter / Carbide Burr
- Hole Saws
- DRILL BIT SET
- Step Drill
- Drill Sharpener
- Impact Bit/set
- Annular Cutter
- Drill Bits
- CARBIDE BURR
- EXTENDED BALL SHAPED Burr
- EXTENDED TREE SHAPE RADIUS END Burr
- CARBIDE BURR SETS
- CYLINDRICAL SQUARE END Burr
- BALL SHAPE Burr
- INVERTED CONE SHAPE Burr
- CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END
- TAPERED RADIUS END Burr
- ALUMINIUM TREE SHAPE RADIUS END Burr
- CONE SHAPE Burr
- OVAL SHAPE Burr
- FLAME SHAPE Burr
- CYLINDRICAL END CUT Burr
- ALUMINIUM OVAL SHAPE Burr
- ALUMINIUM BALL SHAPE Burr
- ALUMINIUM CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END Burr
- ALUMINIUM CYLINDRICAL SQUARE END Burr
- ALUMINIUM TAPERED RADIUS END Burr
- EXTENDED CYLINDRICAL END CUT Burr
- EXTENDED CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END Burr
- EXTENDED TAPERED RABIUS END Burr
- Milling Tools
- Countersink
- Pipe Cutter
- Core Drill
- Glues, Adhesives and Tapes
- Lifting & Handling
- Fasteners
- Sand / Soda Blasting
- Ladder
- Covid Self Test Kit / Sanitiser
- Used Machines
- Fans / Vaccums
- Batteries & Chargers
- GIFT VOUCHERS
- HIRE
- Wheels
- First Aid / Energy Drink
- National Plus
Categories
-
AbrasivesAbrasives
-
3M Abrasives
- 3M™ Belts
- 3M Bonding/Mounting/Transfer Tapes
- 3M Bristle Brushes and Discs
- 3M Compounds & Polishes
- 3M Cubitron™ Cut-Off Discs
- 3M™ Cut-Off Wheels
- Abrasive Sheets & Rolls 3M
- Cubitron™ Fibre Disc
- Cubitron™ Grinding Wheel
- Deburring & Finishing Wheels 3M
- Flap Discs 3M™
- Scotch-Brite™ Clean & Strip Discs
- Scotch-Brite™ Hand Pads
- Scotch-Brite™ Light Grinding and Blending Disc
- Silver Depressed Centre Grinding Wheel
- Backing Pads
- Bevel Brushes
- Clean & Strip DC Discs
- Comidisc / Fine Grinding & Polishing
- Cup Brushes
- Cutting Discs
- Diamond Blades
- Fan Wheels
- Fibre Discs
- Flap Discs
- Flexovit Abrasives
- Grinding Discs
- Hand / Wire Brushes
- Handy Rolls
- Klingspor Abrasives
- Linishing Belt
- Mounted Points
- Norton Abrasives
- Pferd Abrasives
- Pipeline Brushes
- Sanding Discs
- Small Abrasives Mop
- Spindle Mounted Brushes
- Spiral Band
- Tube Brushes
- Wheel Brushes
-
3M Abrasives
- Air Compressors & AccessoriesAir Compressors & Accessories
- Air Tools (Pneumatic Tools)Air Tools (Pneumatic Tools)
- Batteries & ChargersBatteries & Chargers
-
ChemicalsChemicals
- Pickling Paste Gel
- Activators / Cleaners
- Aero Spark
- Aluminium Brightener & Cleaner
- Anti Seize
- Anti Spatters
- Belt Conditioner
- Brake And Parts Cleaner
- Chain & Cable Lube
- Chrome Cote Paint
- Cobra Cote Vinyl Cleaner
- Concrete Dissolver/Remover
- Coolant
- Crack Detector / Dy Check/Flawcheck
- CRC
- Cutting Fluids,Compound
- Cutting, Buffing & Polishing Compounds
- Degreaser & Parts Washer
- Electric Component / Cleaners
- Flece Grease
- Flux Welding
- Gasket Makers & Sealants
- Glass Cleaners
- Grease Fleece Silicone/Lubrication
- Hand Cleaner
- Jet Ski & Boat Marine
- Liquid Spanner
- Marking products
- Molyslip
- Multi Lube Spray
- Multi Purpose Lubricants
- Nozzle Dips
- OIL
- Paint: Cold Galvanising/Silver Gal & Paint
- Rust Remover
- Slipe Slide and Glide
- Stainless Steel & Metal Cleaning Products
- Supa Squirt
- Tape
- Top Guard Gel Coat Treatment
- Truck Wash
- Weld Cleaning
- Woolube
- ClampsClamps
- Covid Self Test Kit / Sanitiser Covid Self Test Kit / Sanitiser
-
Drill / Hole Saws / Annular Cutter / Carbide BurrDrill / Hole Saws / Annular Cutter / Carbide Burr
- Annular Cutter
-
CARBIDE BURR
- ALUMINIUM BALL SHAPE Burr
- ALUMINIUM CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END Burr
- ALUMINIUM CYLINDRICAL SQUARE END Burr
- ALUMINIUM OVAL SHAPE Burr
- ALUMINIUM TAPERED RADIUS END Burr
- ALUMINIUM TREE SHAPE RADIUS END Burr
- BALL SHAPE Burr
- CARBIDE BURR SETS
- CONE SHAPE Burr
- CYLINDRICAL END CUT Burr
- CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END
- CYLINDRICAL SQUARE END Burr
- EXTENDED BALL SHAPED Burr
- EXTENDED CYLINDRICAL END CUT Burr
- EXTENDED CYLINDRICAL RADIUS END Burr
- EXTENDED TAPERED RABIUS END Burr
- EXTENDED TREE SHAPE RADIUS END Burr
- FLAME SHAPE Burr
- INVERTED CONE SHAPE Burr
- OVAL SHAPE Burr
- TAPERED RADIUS END Burr
- Core Drill
- Countersink
- DRILL BIT SET
- Drill Bits
- Drill Sharpener
- Hole Saws
- Impact Bit/set
- Milling Tools
- Pipe Cutter
- Step Drill
- ElectricalElectrical
- Fans / Vaccums Fans / Vaccums
- Fasteners Fasteners
- First Aid / Energy DrinkFirst Aid / Energy Drink
- Gas / Trolleys / Accessories Gas / Trolleys / Accessories
-
Gas Welding : Cutting/ Heating/ Regulators Gas Welding : Cutting/ Heating/ Regulators
- Accessories
- CO2 Heaters / Gas Heaters
- Cutting / Gouging Nozzles
- Cutting Attachments/ Torches
- Flashback Arrestors & Testers
- Gas Cutting Guides
- Gas Cutting Machines
- Gas Fittings
- Gas Hose /Assemblies
- Gas Hose Fittings
- Gas Purging Systems
- Gas Regulators
- Handles
- Harris
- Harris Medical
- Heating Tips
- Heating Torches Kit
- Hose and Cord Reels
- Kits
- Manifold Cylinder /Connection Leads /Scientific Equipment
- Mixers
- Soldering Iron Gas
- Spray Torches
- Supa Heat Heating Barrels
- Swirl Tips
- Thermic Lance Kits
- Welding and Brazing Tips
- GeneratorsGenerators
- GIFT VOUCHERS GIFT VOUCHERS
- Glues, Adhesives and TapesGlues, Adhesives and Tapes
- High Pressure Cleaners / SweepersHigh Pressure Cleaners / Sweepers
- HIREHIRE
- LadderLadder
- Lifting & HandlingLifting & Handling
- Lubrication and Fluid Transfer waxLubrication and Fluid Transfer wax
- Machinery Tools Machinery Tools
- National PlusNational Plus
- Package Deal / Clearance /SalePackage Deal / Clearance /Sale
- Panel Beating & Smash Repair ProductsPanel Beating & Smash Repair Products
-
Safety / PPESafety / PPE
- AntiSlip
- Coveralls
- Eye / Face wear
- Footwear
- General Safety Gear
- Gloves
- Head Protection
- Hearing Protection
- Heavy Duty Umbrella
- High VIS Clothing
- Lincoln
- Respiratory Gear
- Roofers Kits
- Safety Trousers
- Security Padlocks
- Spats And Knee Pads
- Spill Control & Containment
- Sun Protection
- Welding Apron
- Welding Blankets
- Welding Goggles
-
Welding Helmets
- Bossweld Welding Helmet
- Easybeat Welding Helmet
- Kemppi Welding Helmets
- Lincoln Welding Helmet
- Miller Welding Helmet
- Optrel Welding Helmets
- Speedglas™ 3M™ Welding Helmet
- Tecmen Welding Helmets
- Unimig Welding Helmet
- Weldclass Welding Helmets
- Welding Helmet Spare Parts & Accessories
- WIA Welding Helmets
- Welding Hood
- Welding Jackets
- Welding Screens & Frames
- Welding Sleeve
- SaleSale
- Sand / Soda Blasting Sand / Soda Blasting
- Sheet metal Bending and FoldingSheet metal Bending and Folding
- Storage Cabinets Storage Cabinets
-
Tools / Power ToolsTools / Power Tools
- Abbott & Ashby
- ACCUD Tools
- Action Tools
- Alliance Tools
- Alpha/Sterling/AustSaw
- Band Saw Blade
- Bondhus
- Bordo Tools
- BOSCH Tools
- BRAMLEY Tube bender
- Dawn
- DeWALT
- Durum
- Estwing
-
Excision
- Annular Cutters/Core Drills & Accessories Excision
- Bandsaw/Coldsaw/TCT Circular Blades Excision
- Bevellers Excision
- Blades Excision
- Coldsaw Machines
- Coolants Excision
- Industrial Clamps Excision
- Magnetic Based Drills Excision
- Metal Cutting Machines Excision
- Punches and Dies Excision
- Punching Machines Excision
- Taps Excision
- FEIN TOOLS
- FESTOOL
- Garrick
- Geiger Tools
- Hikoki Tools
- Holemaker Magnetic Base Drilling Systems
- Hyundai Power Tools
-
ITM Tools
- Air Compressors ITM
- Air Tools & Accessories ITM
- Benders ITM
- Bevelling Machines ITM
- Brushware
- Brushware ITM
- Clamps ITM
- Cutting Tools ITM
- Drilling Machines ITM
- Engineers Tools ITM
- Fans and Ventilators ITM
- Generators ITM
- Grinding Machines ITM
- Hand Tools ITM
- ITM Complete Product and Price List
- ITM Holemaker
- Lifting & Rigging ITM
- Measuring Tools ITM
- Metal Cutting Saws ITM
- Pressure Washers ITM
- Punches & Shears ITM
- Ratchet Tie Downs ITM
- Sharpening Machines ITM
- Spray Equipments ITM
- Striking Tools ITM
- Vices ITM
- Water Pumps ITM
- Welding Carriages ITM
- WELDING CARRIAGES ITM
- Workshop Storage
- Katana
- KC Tools
-
Kincrome Tools
- Agriculture & Farming Kincrome
- Air Tools & Accessories Kincrome
- Automotive & Vehicle Servicing kincrome
- Construction Kincrome
- Cut, Scrape & Saw kincrome
- File Kincrome
- Kincrome price list
- Lifting & Materials Handling Kincrome
- Lighting & Electrical Kincrome
- Lubrication & Fluid Transfer Kincrome
- Measuring, Marking & Layout Kincrome
- Merchandise & Apparel
- Pliers & Wrenches kincrome
- Power Tools & Accessories Kincrome
- Pressure Washers
- Recreation & Lifestyle
- Screwdrivers & Fastening Kincrome
- Sockets, Socket Sets & Accessories Kincrome
- Spanners & Spanner Sets Kincrome
- Striking & Prying Kincrome
- Tool Boxes & Storage Kincrome
- Tool Kits & Sets Kincrome
- Workshop & Engineering Kincrome
- Klein Tools
- KNIPEX
- Komelon
- Lasquare
- LENOX Tools
- Lufkin
- M7 Air Tools
- Magswitch MSA Magnetics
- Makita Tools
- Mako Tools
- Matson
- Maxigear / Precision
-
Metabo Tools
- 18v CORDLESS METABO
- 18v KIT METABO
- Accessories/Abrasives Metabo
- ANGLE GRINDER 240V METABO
- Batteries Metabo
- Belt Sander Cordless
- Bevelling Tool Metabo
- Burnisher Metabo
- Chargers Metabo
- Die Grinder Cordless
- DRILL 240v METABO
- Heater/ Glue Guns
- Heating Jackets
- Impact Wrenches
- Metal Processing Metabo
- Nail Gun Metabo
- Outdoor Power Equipment Metabo
- Paint Stripper
- Sawing Metabo
- Site Lighting Metabo
- Vacuum Cleaners and extractions Metabo
- Metrinch
- Milwaukee Tools
- Mumme Tools
- National+
- Nitto Kohki
- NPK Tools
- Prowin Tools
- Shinano
- Stanley
- Starrett
- Strong Hand Tools
-
Sutton Tools
- Adaptors SUTTON TOOLS
- Bolt Extractors
- Carbide Burrs Sutton Tools
- Chisels sutton tools
- Clamps Sutton
- Countersinks
- Deburring Sutton Tools
- Die / Die Nuts
- Drill Sets Jobber set
- Drills
- Files & File Sets P&N
- Holesaws Sutton
- Literature
- Measuring Tools P&N
- Pipe Threading Sutton
- Pliers & Wrenches
- Recoil
- Saw Blades CarbiTools
- Screwdriver Bits
- Scribers P&N
- Snips & Shears SUTTON
- Taps
- Teng Tools
- Thor Hammer
- Toledo
- Tolsen Tools
- Warren & Brown
- Used MachinesUsed Machines
-
Welding Accessories & Spare Parts Welding Accessories & Spare Parts
- Balancers
- Cable Connectors
- Chipping Hammers
- Earth/Ground Clamps
- Electrode Holders
- Engineers Chalk / Pencils
- Feed Rollers / Drive Gears
- Flange alignment tools
- Gas Solenoids
- Interconnection Cable
- LEATHER COVER For MIG / TIG / Torch / PLASMA
- Marking
- Pipe Welding Tools
- Purge Gas Retaining Tape for Clean Contaminant-Free Welding / Ceramic Backing Bar
- Spool Hubs
- Tip Cleaners
- Welders Aids Tools
- Welding Cables
- Welding inspection Gauges
- Welding Leads Sets
-
Welding ConsumablesWelding Consumables
-
Electrodes (Welding Rods) ARC / MMA / Stick
- Aluminium Welding Rods 4043
- Cast Iron Welding Rods Ni 55, Ni 98 , Ni 99
- Cellulose Rods E6010 , E6011 , E7010 , E8010
- Dissimilar Metals Steel Welding Rods E312-16
- General Purpose Welding Rods E6012 , E6013
- Hard Facing Solid Welding Rods H350,H600,700,43
- Hydrogen Controlled Welding Rods E7016,E7018
- Iron Powder Welding Rods E7014 , E7024
- Low Alloy Welding Rods E8015, E8018 , E9018
- Stainless Steel MIG Wires ER308, ER309,ER316 Lsi ER2209
- Welding Rod Guard Canister & Hotbox
- Gouging & Hot Rod
- MIG Wires
-
TIG & Gas Filler Rods
- Aluminium Brazing Rods
- Aluminium Bronze Filler Rods
- Aluminium TIG Filler Rods
- Chrome Molybdenum
- De-Oxidised Copper
- Die Steel
- Galvanising Bars
- Manganese Bronze
- Nickel Alloy
- Nickel Bronze
- Phosphor Bronze
- ROD GUARD CANISTERS
- SealCore low temperature Aluminum Tig 0r solder Rod 3.2 mm Dia
- Silicon Bronze Tig/solder
- Silver Brazing Alloys
- Soft Solder
- Stainless Steel TIG Rod
- Steel / Black Mild Steel
- Tobin Bronze
-
Tungsten Electrodes
- Ceriated Tungsten Electrodes
- E3 Tungsten Electrodes 3% Rare Earth
- Lanthanated / Gold / Blue Tungsten Electrodes
- Multi Pack Tungsten Electrodes
- Thoriated Tungsten Electrodes
- Tig Rod / Wire Feeder
- Tungsten Canisters
- Tungsten Sharpeners
- WP2 Green Tungsten Electrodes WITSTAR®
- Zirconiated Tungsten Electrodes
-
Electrodes (Welding Rods) ARC / MMA / Stick
-
Welding Equipment MachinesWelding Equipment Machines
- Bossweld Machines
- BT Welders
- CNC Laser / Plasma
- Duralloy Machines
- Easybeat Machines
- Electrode Ovens
- ESAB Machines
- Foot Controls/Remote Controls
-
Fume Extraction Fans Units
- Allclear / Weldclass Fume Extraction Units
- Binzel Fume Extraction Units
- Bomaksan / Nederman / AWS Fume Extraction units
- BT Fume Extraction Units
- Fanmaster Fume Extraction Units
- ITM Fume Extraction Units
- Keller Fume Extraction Units
- Kemper Fume Extractor
- Lincoln Electric Fume Extraction Units
- Translas Fume Extraction Units
- Unimig Fume Extraction Units
- Induction Welders
- Kemppi Machines
- Laser Welder/Cutter/Seam cleaner/Cleaner
- Lincoln Machines
- Miller Machines
- Pin Insulation Welder
- Pipe welding
- Plastic Welding
- Riland Machines
- Robot Welding Systems
- Rotators Positioners Torch Holders
- Spot Welders
- Steel Vision Machines
- Stud Welders / Studs / Chucks / Stud Guns
- Thermacut Extrafire Plasma Cutters
- Thermocouple Welding Machines
- Trolley
- Tungsten Grinders
-
Unimig Machines
- UNIMIG Air Compressor
- UNIMIG CNC Tables
- UNIMIG Electrode Ovens
- UNIMIG Foot Controls/Remote Controls
- UNIMIG Fume Extraction Unit
- UNIMIG MIG (GMAW) Welders
- UNIMIG MMA (STICK) Welders
- UNIMIG Multi-Process Welders
- UNIMIG Plasma Cutters
- UNIMIG Pulse MIG Welders
- UNIMIG TIG (GTAW) Welders
- UNIMIG Trolleys
- UNIMIG Water Coolers
- Water Coolers / Chillers/coolant
- Weld Cleaning Machine
- Weldclass Machines
- Welding Carriages / Automation
- Welding Table Bench
- WIA Machines
-
Welding Guns, Torches & ConsumablesWelding Guns, Torches & Consumables
- Gouging / Gouging Torches
- i HEAD
- MIG Torch
- MIG Torch Spares Parts
-
Plasma Cutting Torches & Parts
- Air Filters Plasma
- Autogen Ritter Torches
- Binzel Style
- Cebora Style
- Lincoln Plasma Parts
- Plasma Cutting Guides
- Plasma Torch & Parts - Weldclass
- THERMACUT Hypertherm Consumable
- Thermal Dynamics SL60/SL100 Plasma Parts
- Trafimet (Bossweld , Cigweld & Unimig) Plasma Torches
- Unimig Plasma Torches & Parts
- WIA Plasma Torches & Parts
-
TIG Torch Parts
- 17 Series Torch Bodies
- 17/18/26 Series Collet Bodies
- 17/18/26 Series Collet Body Alumina Cups
- 17/18/26 Series Collets
- 17/18/26 Series Gas Lens Alumina Cup
- 17/18/26 Series Gas Lenses
- 17/18/26 Series Insulators
- 18 Series Torch Bodies
- 18/20 Series Parts
- 20 Series Torch Bodies
- 20/24 Series Parts
- 26 Series Parts
- 26 Series Torch Bodies
- 9 Series / 17 Series Parts
- 9 Series Torch Bodies
- 9/17/18/24/26 Series Parts
- 9/17/20/24 Series Parts
- 9/17/24 Series Parts
- 9/20 Series Collet Bodies
- 9/20 Series Collet Body Alumina Cups
- 9/20 Series Collets
- 9/20 Series Gas Lens
- 9/20 Series Gas Lens Alumina Cups
- 9/20 Series Insulators
- Accessory Kits
- Back Caps For Tig 9/17/18/20/26
- Binzel TIG Torch Parts & Consumables
- Clear Pyrex Cup Kits
- MICRO TIG Parts
- Stubby 17/18/26 TIG Setups
- T2 / T3 / T3W Tig Torch Parts
- TIG Fingers
- TIG Spare Parts / Consumables KIT
- TIG Torch Adaptors
- TIG Torch Switches
- TigWare Products
- Unimig TIG Torch Parts & Consumables
- TIG Torches
- WheelsWheels
Understanding the Different Types of Argon for Welding
Date Posted:9 January 2023
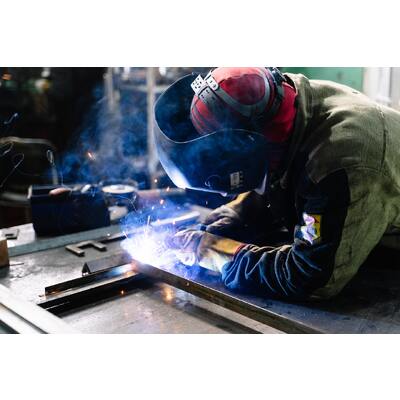


Welding is a critical process in many industries, such as construction and automotive, for joining two pieces of metal together. Argon is an inert gas used in welding to protect the weld from contamination and oxidation.
Argon is defined as a noble gas, which means it is completely chemically inert. This makes it an ideal choice for welding, as it does not react with other elements in the atmosphere or the metal itself. Argon is used in various welding processes, such as metal-inert gas (MIG) welding and tungsten-inert gas (TIG) welding.
While it is the most popular shielding gas for welding, different types of argon are used for various welding processes. Understanding the different kinds of argon and their applications is essential for any welder.
Type 1 - Pure Argon (Ar)
Pure argon is the most common type of argon used in welding. It is used in MIG and TIG welding processes because it provides a protective shield against oxidation and other contaminants. The argon helps to prevent the welded area from becoming contaminated and keeps it free of oxides, which can weaken the weld. Pure argon is also used in gas metal arc welding (GMAW) processes.
Type 2 - Different Argon Mixtures
Argon-oxygen mixtures combine gases used in welding processes that require more heat. Oxygen is added to the argon, creating a more stable and powerful arc that can be used on thicker metals such as aluminium and stainless steel. This arc is well-suited for welding in tight spaces and gives welders an extra heat boost to complete their work.
Welding with an argon-nitrogen mixture allows for a higher heat input than just argon alone. This mixture is often used for welding thicker materials, or in tight locations where increased heat input is necessary. Adding nitrogen to argon creates a more stable arc and provides an improved welding experience. This type of argon is ideal for welding carbon steel and stainless steel.
Argon and hydrogen can be combined to create a welding gas that increases the heat input of welding applications. This combination is beneficial when welding thicker materials or in tight spaces. When used together, argon and hydrogen create a more stable arc and generate a higher heat input, which can be beneficial for welding aluminium and stainless steel.
Conclusion
Welders must understand the different types of argon used for welding, such as pure argon, argon-helium mixtures, and argon-carbon dioxide mixtures. Pure argon is often used in thin metal welding. In contrast, argon-helium mixtures may be used in medium-thick metal welding, and argon-carbon dioxide mixtures may be used in thicker metal welding. Each mixture has its advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the difference between them can help welders to choose the suitable shielding gas for the right type of welding application.
For welding supplies in Australia, check out National Welding and Industrial Supplies. We are the leading welding equipment supplier, so you can expect only the best from us. Explore our collection of modern welding equipment and place your order today!

.png)